18 km SSW of Hualien City, Taiwan
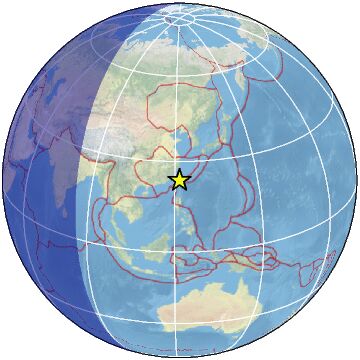





The April 2, 2024, M 7.4 earthquake on the eastern coast of Taiwan occurred as the result of reverse faulting near the boundary between the Eurasia and Philippine Sea plates. The earthquake was followed by a M 6.5 aftershock 13 minutes later. The M 7.4 earthquake occurred in a zone of tectonic transition from eastward-oriented subduction of the Eurasia plate to westward-oriented subduction of the Philippine Sea plate. Focal mechanism solutions for the earthquake indicate that rupture occurred on a northeast-southwest-striking, moderately dipping, reverse fault. Given the location, depth, and mechanism of the earthquake, it is likely associated with faulting within the Eurasia plate, above the subduction zone interface. At the location of the earthquake, the Philippine Sea plate is moving northwest with respect to the Eurasian plate at a velocity of about 78 mm/yr.
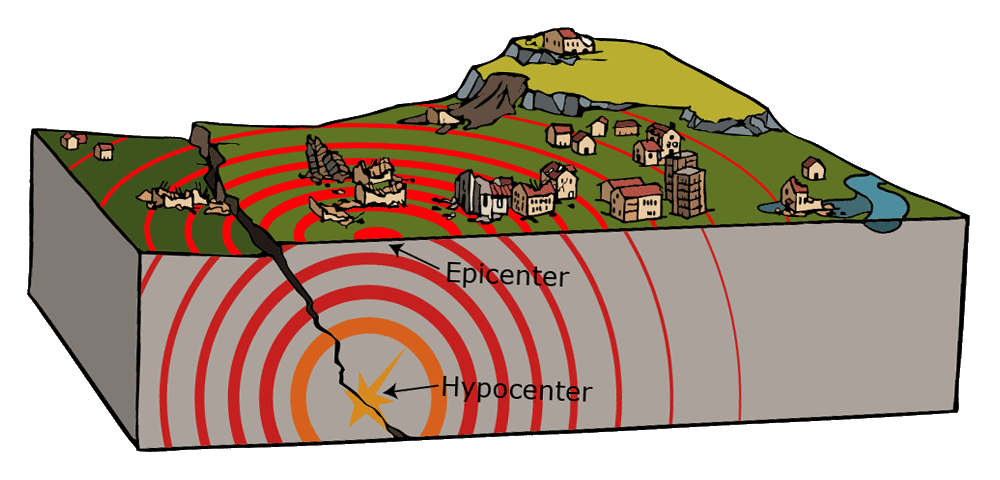
While commonly plotted as points on maps, earthquakes of this size are more appropriately described as slip over a larger fault area. Reverse faulting events of the size of the April 2, 2024, earthquake are typically about 60 by 35 km in size (length x width).
This tectonically complex region has historically produced many other large earthquakes of M 7+. Over the preceding 50 years, six other M7+ earthquakes have occurred within 250 km of the April 2, 2024, earthquake. The largest of these was an M 7.7 earthquake in September 1999 (the Chi-Chi earthquake) that resulted in at least 2,297 fatalities, caused damage estimated at $14 billion, and occurred 59 km west of the April 2, 2024, event. In 1920, a magnitude 8.2 earthquake, potentially associated with the subduction zone interface between the Philippine Sea and Eurasia plates, occurred immediately east of the April 2 earthquake.
Землетрясение — это серьезное геофизическое явление, которое вызывается движением плит земной коры. Когда давление в земле становится слишком высоким или слишком низким, плиты могут двигаться, вызывая растрескивание, растяжение или сжатие земли в определенных местах.
Земная кора состоит из семи больших плит, также известных как континентальные плиты. В дополнение к континентальным плитам существует около 50 более мелких плит. Когда происходит движение плит, возникают вибрации, которые могут протягиваться на большие расстояния и вызывать ущерб инфраструктуре, зданиям и жизням людей. Некоторые землетрясения могут быть очень слабыми и практически незаметными для населения, но другие могут быть очень сильными и причинять серьезный ущерб людям.
Причины землетрясений могут варьироваться, включая вулканическую активность, столкновение земных плит. Так-же землетрясения могут быть вызваны деятельностью человека, такой как добыча нефти или газа, или строительство гидроэлектростанций.